
Differences Between Type Aliases and Interfaces TypeScript is only concerned with the structure of the value we passed to printCoord - it only cares that it has the expected properties.īeing concerned only with the structure and capabilities of types is why we call TypeScript a structurally typed type system. Just like when we used a type alias above, the example works just as if we had used an anonymous object type. When a value is of type any, you can access any properties of it (which will in turn be of type any), call it like a function, assign it to (or from) a value of any type, or pretty much anything else that’s syntactically legal: TypeScript also has a special type, any, that you can use whenever you don’t want a particular value to cause typechecking errors. Note that is a different thing refer to the section on Tuples. We’ll learn more about the syntax T when we cover generics.

You may also see this written as Array, which means the same thing. string is an array of strings, and so on). To specify the type of an array like, you can use the syntax number this syntax works for any type (e.g. Always use string, number, or boolean for types.
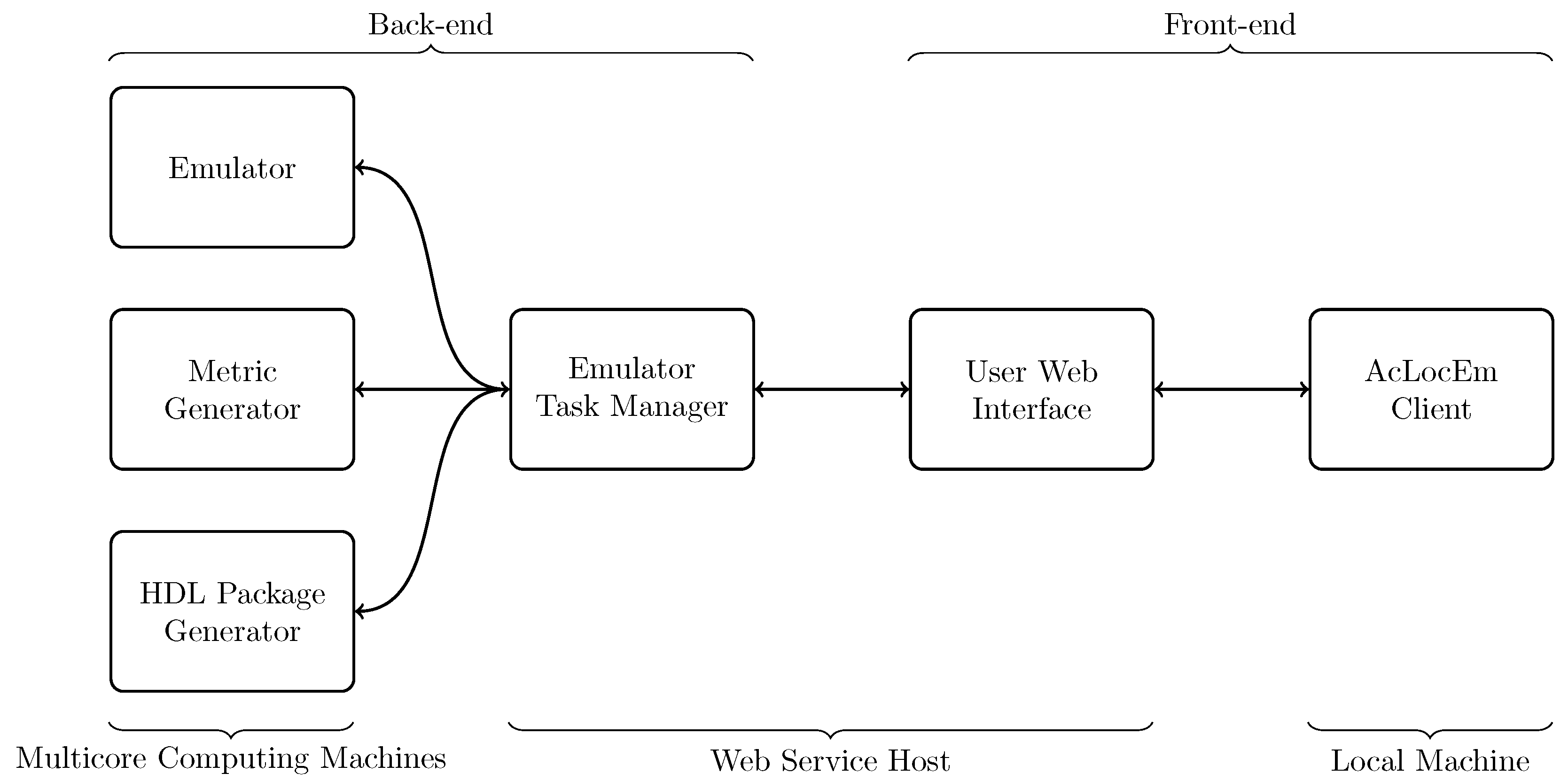
The type names String, Number, and Boolean (starting with capital letters) are legal, but refer to some special built-in types that will very rarely appear in your code.
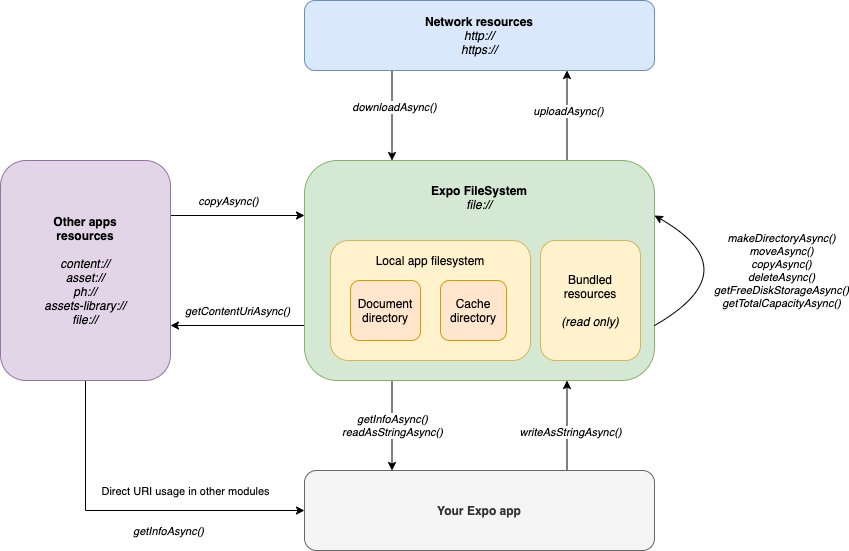
JS JSON JSON Intro JSON Syntax JSON vs XML JSON Data Types JSON Parse JSON Stringify JSON Objects JSON Arrays JSON Server JSON PHP JSON HTML JSON JSONP JS AJAX AJAX Intro AJAX XMLHttp AJAX Request AJAX Response AJAX XML File AJAX PHP AJAX ASP AJAX Database AJAX Applications AJAX Examples JS Web APIs Web API Intro Web Forms API Web History API Web Storage API Web Worker API Web Fetch API Web Geolocation API JS Browser BOM JS Window JS Screen JS Location JS History JS Navigator JS Popup Alert JS Timing JS Cookies JS HTML DOM DOM Intro DOM Methods DOM Document DOM Elements DOM HTML DOM Forms DOM CSS DOM Animations DOM Events DOM Event Listener DOM Navigation DOM Nodes DOM Collections DOM Node Lists JS Async JS Callbacks JS Asynchronous JS Promises JS Async/Await

JS Classes Class Intro Class Inheritance Class Static JS Functions Function Definitions Function Parameters Function Invocation Function Call Function Apply Function Closures JS Objects Object Definitions Object Properties Object Methods Object Display Object Accessors Object Constructors Object Prototypes Object Iterables Object Sets Object Maps Object Reference JS Versions JS Versions JS 2009 (ES5) JS 2015 (ES6) JS 2016 JS 2017 JS 2018 JS IE / Edge JS History JS Tutorial JS HOME JS Introduction JS Where To JS Output JS Statements JS Syntax JS Comments JS Variables JS Let JS Const JS Operators JS Arithmetic JS Assignment JS Data Types JS Functions JS Objects JS Events JS Strings JS String Methods JS String Search JS String Templates JS Numbers JS Number Methods JS Arrays JS Array Methods JS Array Sort JS Array Iteration JS Array Const JS Dates JS Date Formats JS Date Get Methods JS Date Set Methods JS Math JS Random JS Booleans JS Comparisons JS Conditions JS Switch JS Loop For JS Loop For In JS Loop For Of JS Loop While JS Break JS Iterables JS Sets JS Maps JS Typeof JS Type Conversion JS Bitwise JS RegExp JS Errors JS Scope JS Hoisting JS Strict Mode JS this Keyword JS Arrow Function JS Classes JS JSON JS Debugging JS Style Guide JS Best Practices JS Mistakes JS Performance JS Reserved Words


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
